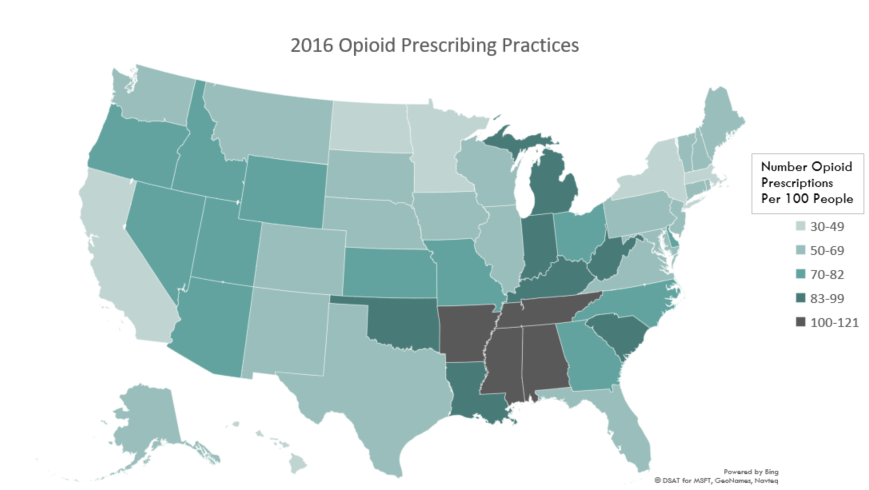
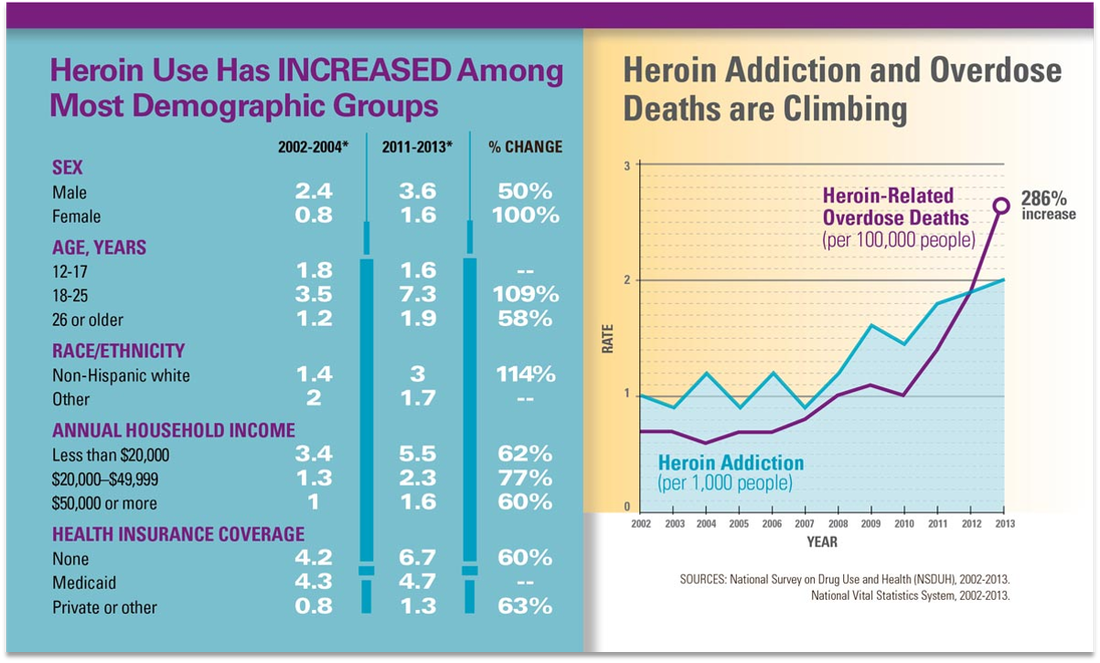
The world and the nation is facing an opioid epidemic and people are dying every day
As reported by the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), the United States is in the midst of an opioid overdose epidemic with every American state, county, socio-economic and ethnic group impacted.
Drug overdose is the leading cause of accidental death in the United States. Killing more people than car accidents and guns – 63,600 Americans died from drug overdoses in 2016. Opioids account for more than 66% of all overdose deaths – killing more than 42,000 people in 2016.